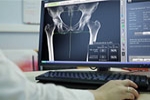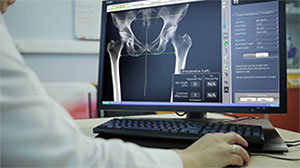
Robotic surgery or robot-assisted surgery is the use of cutting-edge robotic systems controlled by a skilled surgeon to perform surgical procedures. These advanced systems provide the surgeon with a high degree of stability, precision, and control. Several orthopedic procedures such as joint replacement can now be done using robotic technology.
Some advantages of robotic surgery include:
- Pre-Surgical Planning: Using CT scan images fed into the robotic system, the surgeon can plan out ahead of time exactly where an implant is going to be placed. The robotic arm can then be programmed to operate only within a precise well-demarcated area for better patient safety.
- Improved Visibility: The robotic system includes a high-definition camera which provides the surgeon with a magnified 3D view of the patient’s anatomy while performing the surgery.
- Better Control: The ability to filter out faint physiologic tremors of the surgeon’s hand makes the robotic arm very stable. This reduces the risk of errors while performing complex and delicate procedures.
- Greater Dexterity: The greater flexibility of the robotic arm gives the surgeon better angles and more freedom to work through small surgical incisions minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- More Precision: Computer guidance and robotic arm assistance can facilitate precise implant placement with a high degree of accuracy and reproducibility.
- Fewer complications: As robotic surgeries are usually performed minimally invasively, there is less risk of postsurgical complications of such as pain, infection, and delayed healing.
- Better Surgical Outcomes: With precise placement of implants, the patient’s natural anatomy is reproduced. This allows tendons, ligaments, and muscles around the joint to function more normally. Patients are thus able to recover quickly and return to their routine activities.
American Hip Institute was the first in the nation to perform outpatient robotic hip replacement surgery. With continued advances in technology such as haptics (tactile sensing), better visualization, and development of smaller robotic arms; the scope of robotic surgery is likely to expand further helping more surgeons achieve and maintain a high level of precision during surgery.